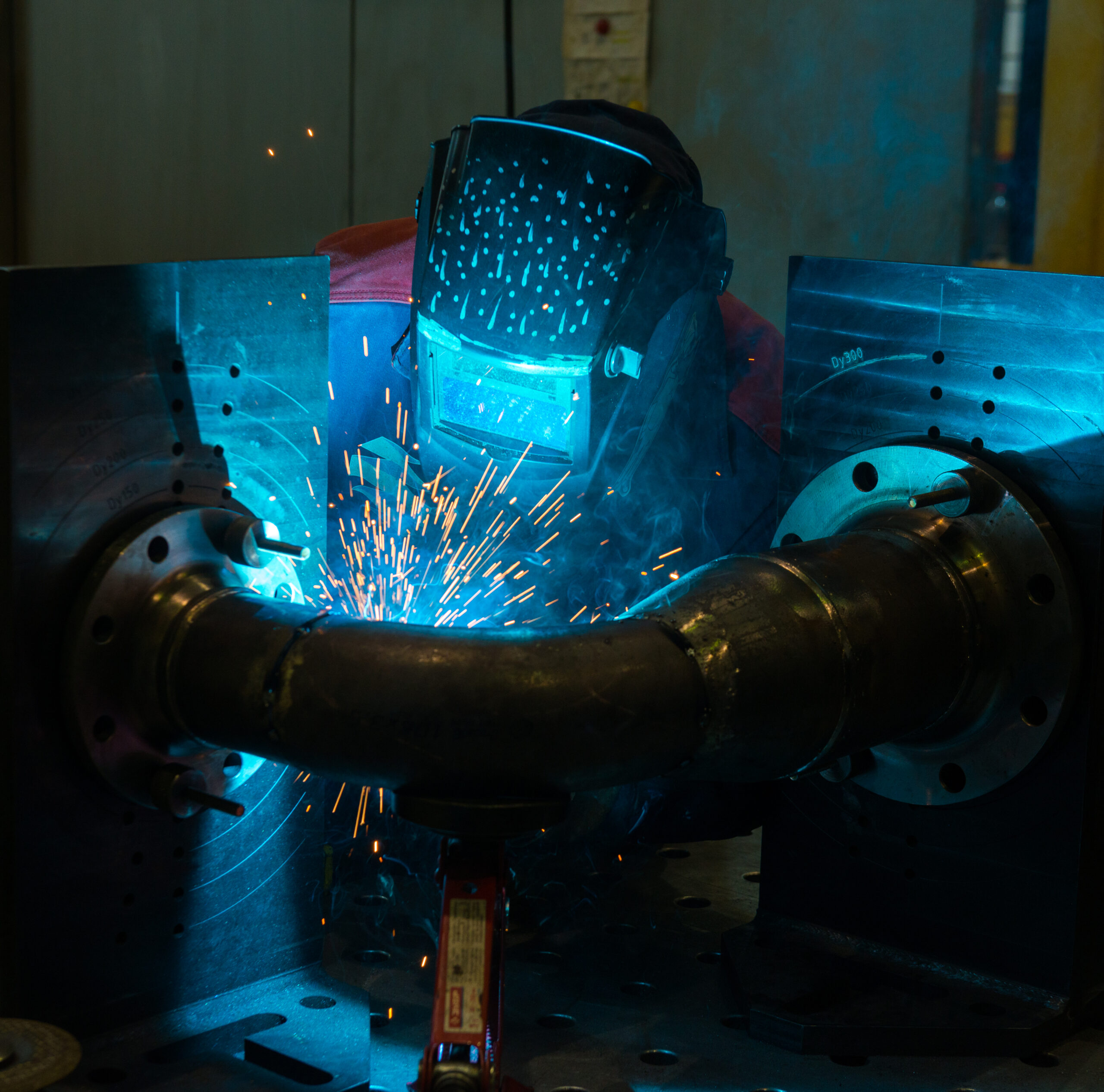
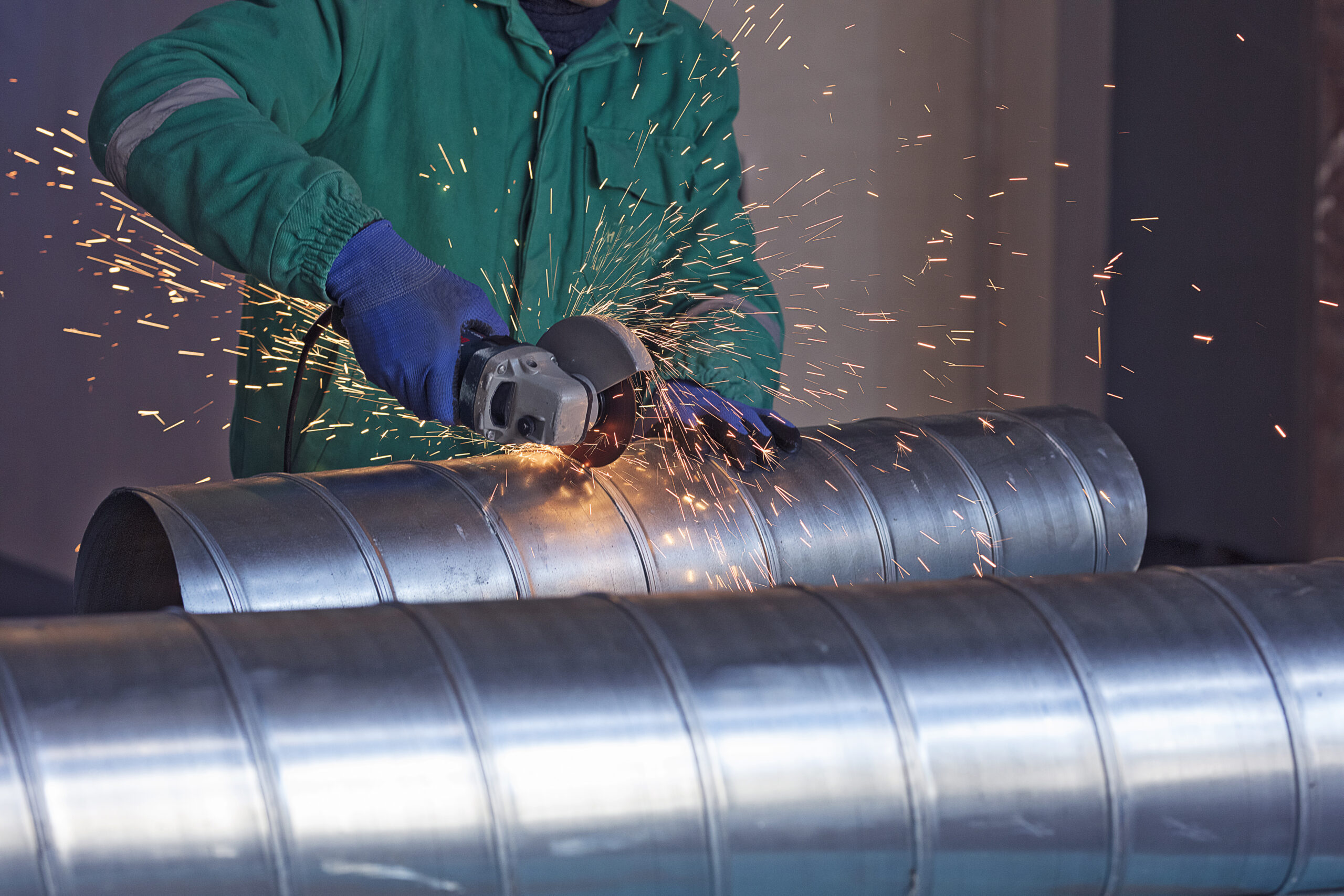
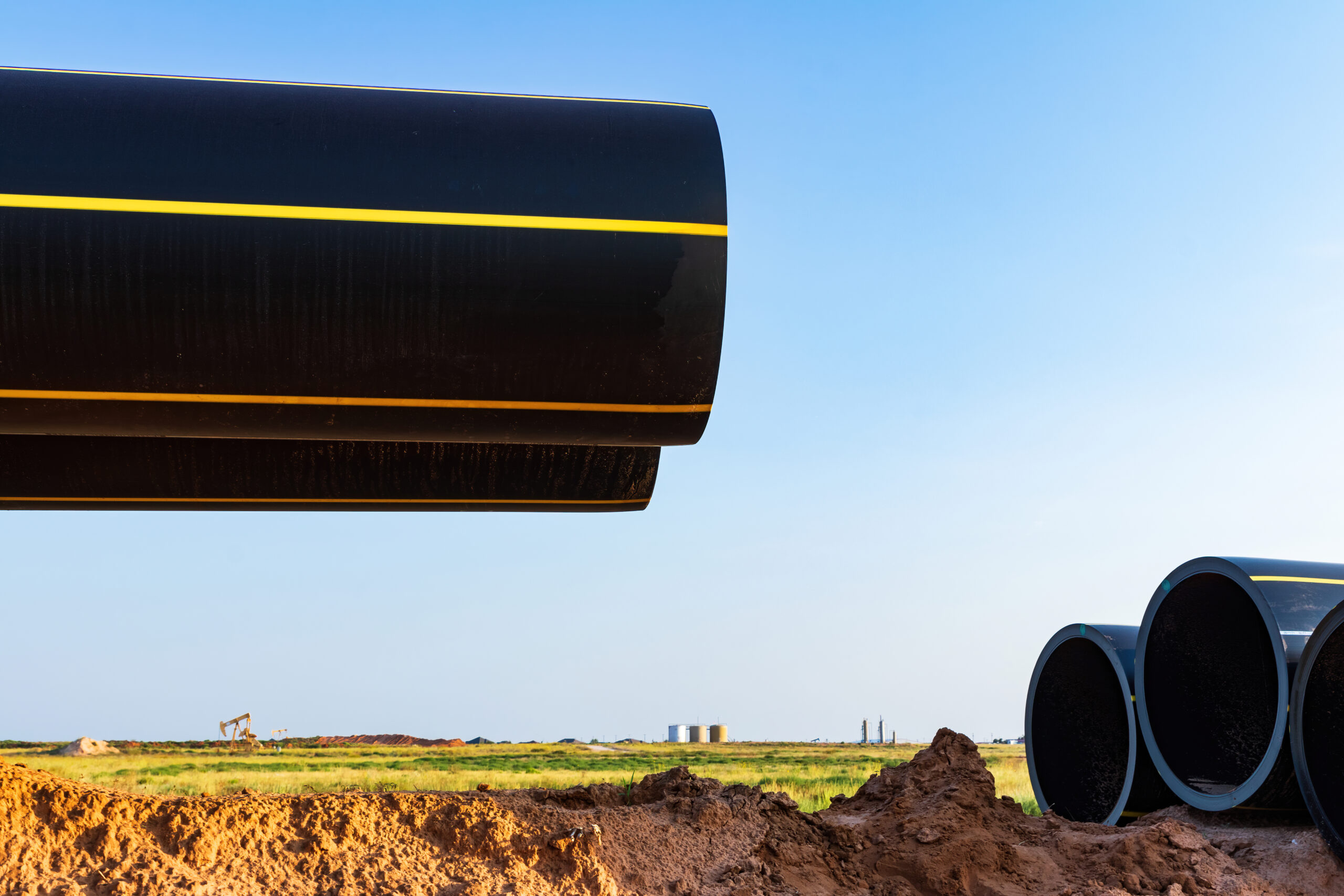
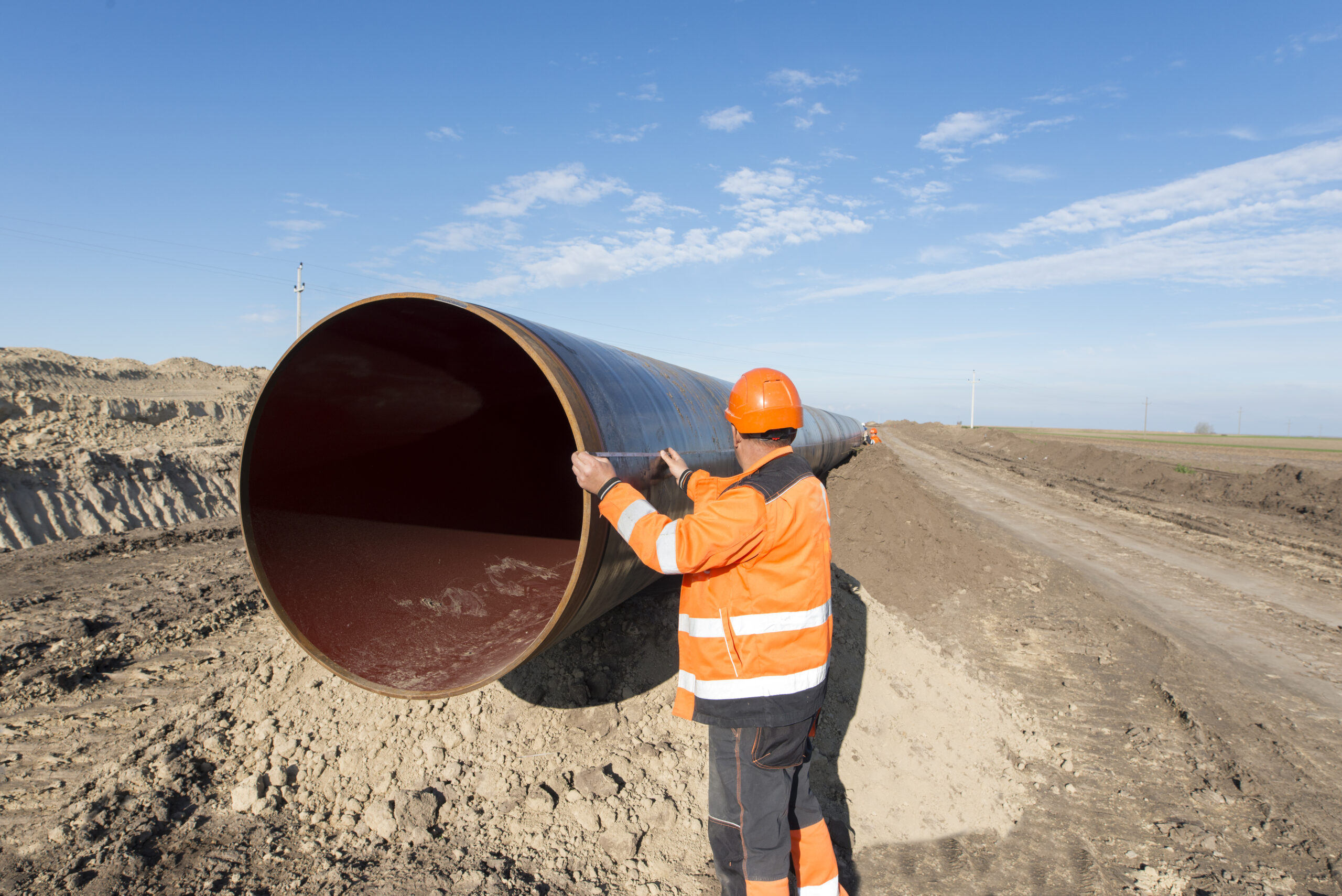
What is pipe cladding?
Pipe cladding, also known as pipe lining or pipe coating, is used to enhance the durability and performance of pipes in various industries, including the oil and gas industry, petrochemicals, water supply, and mining. The process involves applying a protective layer on the external surface of pipes to safeguard them against corrosive substances, abrasive materials, and other environmental factors that could lead to deterioration and failure.
However, exposure to harsh environments and corrosive substances can cause wear and tear, compromising the structural integrity of these pipelines. Engineers and experts have developed a reliable solution known as pipe cladding to combat this issue.
Read: “Pipe Chocks: What are They and How They Work?”
Why is it Needed?
Pipes play a crucial role in transporting fluids and gases over long distances. However, many of these pipelines are exposed to harsh conditions above and below ground. Factors such as soil corrosivity, chemical interactions, high pressures, and temperature fluctuations can lead to corrosion and weakening of the pipe material over time.
This not only compromises the structural integrity of the pipes but also poses significant safety and environmental risks.
What Is the Pipe Cladding Process?
It involves bonding a protective layer onto the pipe’s external surface. People use various cladding materials, with common choices like stainless steel, nickel, and corrosion-resistant alloys. The selection of the cladding material depends on the specific environment and application requirements.
Moreover, different methods of applying cladding include welding, explosive bonding, and roll bonding. Welding is a widely used technique where the cladding material is melted and fused onto the pipe’s surface.
Furthermore, explosive bonding involves placing the cladding material over the pipe surface and using explosives to bond them. Roll bonding uses pressure to roll the cladding material onto the pipe.
The pipe cladding process typically involves these steps:
- Surface Preparation: Before applying the protective layer, the surface of the pipe must be thoroughly cleaned to remove any contaminants or impurities. Thus, this step ensures proper adhesion of the cladding material to the pipe’s surface.
- Choice of Cladding Material: Various materials can be used for pipe cladding, such as polymers, plastics, metals, ceramics, and composites. The selection of the cladding material depends on the specific application and the environment in which the pipe will operate.
- Application Techniques: Pipe cladding can be achieved through various methods, including hot-dip galvanizing, fusion-bonded epoxy (FBE) coating, thermal spray, extrusion, and adhesive bonding. Each technique offers unique advantages and is chosen based on cost, complexity, and the properties of the cladding material.
- Quality Control: To ensure the effectiveness of the cladding, strict quality control measures are implemented throughout the process. This involves inspections, testing, and adherence to industry standards and regulations.
Benefits of Pipe Cladding
Corrosion Protection
Pipeline Corrosion is one of the most significant threats to pipeline integrity. Pipe cladding is a barrier against corrosive agents, preventing direct contact with the base material. Thus, this protective layer ensures the pipeline remains corrosion-resistant, even when exposed to aggressive substances.
Abrasion and Erosion Resistance
In industries where pipelines transport abrasive materials, erosion, and abrasion can cause substantial damage over time. Pipe cladding with wear-resistant materials mitigates the effects of abrasion and corrosion, increasing the pipeline’s longevity and reducing maintenance needs.
Chemical Resistance
Different pipelines handle various fluids and gases, some of which can be highly reactive or chemically aggressive. By selecting appropriate cladding materials, engineers can protect the pipeline from chemical damage, ensuring safe and reliable operation.
Mechanical Strength
Pipe cladding can enhance the mechanical strength of a pipeline, making it more robust and capable of withstanding higher pressures and loads. This is particularly important in critical applications where failure could have severe consequences.
Temperature and Thermal Stability
Extreme temperatures can affect the structural integrity of pipelines. Moreover, cladding materials can provide thermal stability, allowing channels to operate efficiently and safely in high or low-temperature environments.
Types of Pipe Cladding
Metal Cladding
Metal cladding involves applying a metal layer onto the pipe’s surface using various methods such as welding, explosion bonding, or roll bonding. Typical metals used for cladding include stainless steel, nickel alloys, aluminum, and titanium.
Polymer Cladding
Polymer cladding involves coating the pipeline with specialized polymer materials. Industries often use this type of cladding for chemical resistance and anti-corrosion purposes.
Concrete Cladding
In certain situations, pipelines may require concrete cladding to provide protection against external forces and buoyancy or meet specific construction requirements.
Application of Pipe Cladding
Oil and Gas Industry
The oil and gas sector extensively uses pipe cladding to protect offshore and onshore drilling, transportation, and refining pipelines. Cladding helps prevent internal pipeline corrosion caused by the harsh marine environment and corrosive substances in the oil and gas.
Chemical and Petrochemical Industry
Pipe cladding is commonly applied in chemical and petrochemical plants to protect pipelines carrying aggressive chemicals and corrosive substances.
Mining Industry
In mining operations, pipelines can be exposed to abrasive materials and harsh conditions. Pipe cladding helps prevent corrosion, erosion and extends the life of mining pipelines.
Water and Wastewater Management
Cladding protects against corrosion and enhances longevity for water distribution and wastewater pipelines.
Conclusion
Pipe cladding is a vital technique to ensure the integrity and durability of pipelines in various industries. By applying a protective layer to pipelines, engineers can safeguard them against corrosion, erosion, chemical damage, and mechanical stress.
Thus, it leads to safer operations, reduced maintenance costs, and extended pipeline lifespan. Moreover, as industries continue to evolve, advancements in pipe cladding technology will play an increasingly significant role in maintaining the efficiency and reliability of critical infrastructure. For any pipeline service, contact Lined Pipe System now!
FAQs
Q1: Why is pipe-cladding necessary?
It is necessary to protect pipes from corrosion, abrasion, and other damaging factors, ensuring their longevity and preventing leaks or failures.
Q2: What materials are used for pipe-cladding?
Depending on the application and environmental conditions, it can utilize various materials, such as polymers, plastics, metals, ceramics, and composites.
Q3: How is pipe cladding applied?
These methods include hot-dip galvanizing, fusion-bonded epoxy (FBE) coating, thermal spray, extrusion, and adhesive bonding.
Q4: What are its benefits?
The benefits include corrosion protection, abrasion resistance, chemical resistance, thermal insulation, and environmental protection.
Q5: In which industries are pipe-cladding commonly used?
In industries such as oil and gas, petrochemicals, water treatment, and other sectors where pipes transport fluids and gases. Therefore, it sees widespread use.
Q6: How does pipe-cladding contribute to sustainability?
By extending the life of pipes and reducing maintenance needs, it promotes sustainability by minimizing material waste and environmental impacts.
Q7: Can pipe-cladding enhance a pipeline’s mechanical strength?
Yes, It can enhance a pipeline’s mechanical strength, making it more resilient and capable of withstanding higher pressures and loads.